NPN Transistor
A transistor in which one p-type material is placed between two n-type materials.1 Comment
1 Star
Various White Carbonite Freezer
Design a circuit that detects the presence of the infrared signal. The circuit should light a red LED when infrared signal is detected otherwise it should light a green LED. You may use NPN transistors, IR LED, Photodiode, Red LED, Green LED and a rectifier diode.... show more18 Comments
1 Star
NPN-TRANS-002
The Ariel AI Chip, a state-of-the-art integrated circuit designed for high-performance computing applications, incorporates an innovative architecture that leverages radical transistor technology to optimize AI and machine learning tasks. At the heart of this chip lies a quad-core CPU operating at a clock speed of 2GHz, distinguished by its part number CPU-RT-4C-2G. The chip's power management is efficiently handled by a DC power supply, specified as DCPS-5V, ensuring a stable 5V input. Key to its operation are two NPN transistors, identified by part numbers NPN-TRANS-001 and NPN-TRANS-002, which, along with a pair of 1kΩ resistors (RES-1K and RES-1K-002) and a 10µF capacitor (CAP-10UF), form the critical signal processing and conditioning circuitry. This assembly is designed for seamless integration into advanced computing systems, particularly those focused on Flux AI environments, where its performance and efficiency can be fully leveraged. The Ariel AI Chip sets a new benchmark in AI computing, offering unparalleled processing power and efficiency for cutting-edge applications.... show more16 Comments
1 Star
RES-1K
The Ariel AI Chip, a pioneering component in the realm of artificial intelligence hardware, integrates a suite of electronic elements tailored for high-performance computing applications. At the heart of this assembly lies a CPU with a Radical Transistor architecture, featuring a quad-core setup clocked at 2GHz, identified by the part number CPU-RT-4C-2G. Power management is facilitated through a DC Power Supply, marked DCPS-5V, ensuring a stable 5V supply to the intricate circuitry. The chip's switching capabilities are bolstered by two NPN transistors, NPN-TRANS-001 and NPN-TRANS-002, which play a crucial role in signal modulation. Essential to the chip's operation are the passive components: two 1kΩ resistors (RES-1K and RES-1K-002) and a 10µF capacitor (CAP-10UF), which together with the transistors, form a robust network ensuring reliable performance under varying load conditions. Designed for integration into advanced AI systems, this chip stands out for its innovative use of standard components in a configuration that emphasizes efficiency, reliability, and high-speed data processing capabilities.... show more1 Comment
1 Star
DCPS-5V
The Ariel AI chip prototype, designed for integration with Flux AI for advanced simulation and testing, incorporates a suite of electronic components optimized for high-performance computing applications. At the heart of this system lies a CPU with a radical transistor architecture, featuring a 4-core configuration and a clock speed of 2GHz, identified by part number CPU-RT-4C-2G. Power management is facilitated through a DC Power Supply, specified as DCPS-5V, ensuring a stable 5V supply to the system. The circuit's dynamic performance is modulated by two NPN transistors, NPN-TRANS-001 and NPN-TRANS-002, which, along with precision resistors RES-1K and RES-1K-002 (both 1kΩ), and a 10μF capacitor (CAP-10UF), form the critical signal processing path leading to the CPU. This configuration is designed to provide an efficient, reliable processing environment for AI computations, with an emphasis on minimizing latency and maximizing throughput. The Ariel AI chip's architecture, combining traditional components with an innovative CPU design, offers a versatile platform for developing advanced AI applications, reflecting a significant step forward in computational technology.... show more1 Comment
1 Star
RES-1K-002
The Ariel AI Chip, a pioneering component in the field of artificial intelligence hardware, integrates advanced features designed to enhance computational efficiency and AI processing capabilities. This chip is distinguished by its utilization of a quad-core CPU with a clock speed of 2GHz, operating on a radical transistor architecture that promises significant improvements in speed and power efficiency. Key components that constitute the Ariel AI Chip include a DC power supply with a 5V output (DCPS-5V), NPN transistors (NPN-TRANS-001 and NPN-TRANS-002) that serve as the fundamental switching elements, precision resistors (RES-1K and RES-1K-002) each with a resistance of 1kΩ, and a capacitor (CAP-10UF) rated at 10μF to stabilize voltage and filter noise. This chip is designed for integration into systems requiring advanced AI capabilities, offering a comprehensive solution for developers looking to leverage machine learning and artificial intelligence in their applications. With its innovative architecture and component selection, the Ariel AI Chip stands out as a versatile and powerful tool for a wide range of AI applications, from embedded systems to more complex computational platforms.... show more1 Comment
1 Star
CPU-RT-4C-2G
The Ariel AI Chip, an innovative component designed for high-performance computing applications, integrates a sophisticated array of electronic parts to deliver unparalleled processing capabilities. At the heart of this system is a CPU with a radical transistor architecture, featuring a core count of 4 and a clock speed of 2GHz, identified by its part number CPU-RT-4C-2G. Power management within the chip is efficiently handled by a DC Power Supply, rated at 5V, with the part number DCPS-5V, ensuring stable and reliable operation. The chip's signal processing and amplification needs are addressed through the inclusion of two NPN transistors, with part numbers NPN-TRANS-001 and a similar variant, providing the necessary gain and switching capabilities for complex computational tasks. Signal conditioning is further enhanced by a pair of 1kΩ resistors, RES-1K and RES-1K-002, and a 10µF capacitor, CAP-10UF, which work together to filter and stabilize the power supply and signal pathways, ensuring clean and noise-free operation. This integration of components within the Ariel AI Chip offers electrical engineers a robust platform for developing advanced AI systems, combining high processing power with efficient power management and signal integrity, suitable for a wide range of applications in the field of artificial intelligence.... show more1 Comment
1 Star
CAP-10UF
The Ariel AI chip prototype is an advanced electronic component designed for integration into the Flux AI environment, facilitating simulation and testing of AI applications. This component features a collection of carefully selected parts including a DC power supply (DCPS-5V), NPN transistors (NPN-TRANS-001 and NPN-TRANS-002), resistors (RES-1K and RES-1K-002), a capacitor (CAP-10UF), and a cutting-edge CPU (CPU-RT-4C-2G) with a 4-core architecture, operating at a clock speed of 2GHz. The CPU's innovative radical transistor architecture is specifically tailored for high-performance computing tasks associated with AI and machine learning applications. This configuration ensures efficient power management, signal processing, and data flow within the chip, making it an ideal choice for developers and engineers looking to push the boundaries of AI technology. The inclusion of standard components like NPN transistors, resistors, and capacitors, alongside the specialized CPU, allows for a versatile and robust design, suitable for a wide range of AI applications.... show more1 Star
NPN-TRANS-001
The Ariel AI chip prototype is an advanced electronic component designed to enhance the capabilities of Flux AI systems through a sophisticated arrangement of transistors, resistors, capacitors, and a cutting-edge CPU. Key components include two NPN transistors (part numbers NPN-TRANS-001 and NPN-TRANS-002), which are essential for signal amplification, alongside precision resistors (RES-1K and RES-1K-002) each with a resistance of 1kΩ, and a capacitor (CAP-10UF) with a capacitance of 10μF, crucial for filtering and stabilizing the voltage supply. At the heart of the design is a revolutionary CPU (part number CPU-RT-4C-2G) featuring a quad-core setup with a clock speed of 2GHz, based on a radical transistor architecture, designed to deliver unparalleled computational performance for AI tasks. This component set is powered by a 5V DC power supply (DCPS-5V), ensuring a stable and efficient operation. The Ariel AI chip is engineered for high-speed, reliable performance in demanding AI applications, representing a significant advancement in electronic component design for artificial intelligence systems.... show more1 Star
Realistic Brown Battle Mech
Nice — you can do a clean pulse + latch using a single quad Schmitt-NAND chip: 74HC132 (or 74LVC132 for 3.3 V systems). The HC132 contains four 2-input NAND gates with Schmitt inputs so you can both clean a noisy SYN480R DATA line and build an SR latch (NAND SR is active-LOW) inside one package. Only a few passives and a driver transistor are needed. Below is a ready-to-build recipe (parts, wiring, explanation, tuning tips, and an ASCII schematic) — no extra logic ICs required. Parts (per latch) 1 × 74HC132 (quad 2-input NAND with Schmitt inputs). If your system is 3.3 V use 74LVC132 / 74HC132 rated for 3.3 V. Rin = 47 kΩ (input series) Cfilter = 10 nF (input RC to ground) — tweak for debounce/clean time Rpulldown = 100 kΩ (pull-down at input node, optional) Rpullup = 100 kΩ (pull-up for active-LOW R input so reset is idle HIGH) Rbase = 10 kΩ, Q = 2N2222 (NPN) or small N-MOSFET (2N7002) to drive your load Diode for relay flyback (1N4001) if you drive a coil Optional small cap 0.1 µF decoupling at VCC of IC Concept / how it works (short) Use Gate1 (G1) of 74HC132 as a Schmitt inverter by tying its two inputs together and feeding a small RC filter from SYN480R.DATA. This removes HF noise and provides a clean logic transition. Because it's a NAND with tied inputs its function becomes an inverter with Schmitt behavior. Use G2 & G3 as the cross-coupled NAND pair forming an SR latch (active-LOW inputs S̄ and R̄). A low on S̄ sets Q = HIGH. A low on R̄ resets Q = LOW. Wire the cleaned/inverted output of G1 to S̄. A valid received pulse (DATA high) produces a clean LOW on S̄ (because G1 inverts), setting the latch reliably even if the pulse is brief. R̄ is your reset input (pushbutton, HT12D VT, MCU line, etc.) — idle pulled HIGH. Q drives an NPN/MOSFET to switch your load (relay, LED, etc.). Recommended wiring (pin mapping, assume one chip; use datasheet pin numbers) I’ll refer to the 4 gates as G1, G2, G3, G4. Use G4 optionally for additional conditioning or to build a toggler later. SYN480R.DATA --- Rin (47k) ---+--- Node A ---||--- Cfilter (10nF) --- GND | Rpulldown (100k) --- GND (optional, keeps node low) Node A -> both inputs of G1 (tie inputs A and B of Gate1 together) G1 output -> S̄ (S_bar) (input1 of Gate2) Gate2 (G2): inputs = S̄ and Q̄ -> output = Q Gate3 (G3): inputs = R̄ and Q -> output = Q̄ R̄ --- Rpullup (100k) --- VCC (reset is idle HIGH; pull low to reset) (optional) R̄ can be wired to a reset pushbutton to GND or to an MCU pin Q -> Rbase (10k) -> base of 2N2222 (emitter GND; collector to one side of relay coil) Other side of relay coil -> +V (appropriate coil voltage) Diode across coil If you prefer MOSFET low side switching: Q -> gate resistor 100Ω -> gate of 2N7002 2N7002 source -> GND ; drain -> relay coil low side... show more1 Star
NPN Transistor
A transistor in which one p-type material is placed between two n-type materials.1 Comment
NPN Transistor
A transistor in which one p-type material is placed between two n-type materials.NPN Transistor
A transistor in which one p-type material is placed between two n-type materials.NPN Transistor 0aa2
A transistor in which one p-type material is placed between two n-type materials.1 Comment
FJD5553TM 0ca6 4073
Bipolar (BJT) Transistor NPN - Surface Mount TO-252AA. #CommonPartsLibrary #TransistorBJT #FJD55531 Comment
2SC5200-O(Q)
Bipolar (BJT) Transistor NPN 230V 15A 30MHz 150W Through Hole TO-3P(L) #CommonPartsLibrary #TransistorBJT #2SC52001 Comment
Fast Silver Flubber
Create a schematic diagram of an electric fence controller using the NE556 dual timer IC. The circuit must include all components with clear electronic symbols (resistors, capacitors, transistors, diode, relay) connected by lines as in a real circuit diagram. Specifications: 1. Power supply: - Vcc = +12V connected to pin 14 of the NE556. - Pin 1 of the NE556 to ground. 2. Timer A (active 10 seconds): - Pin 2 (Trigger A) receives a pulse from transistor Q2 (contact detector). - Pin 6 (Threshold A) connected to Pin 7 (Discharge A). - R1 = 1 MΩ between Pin 7 and +12V. - C1 = 10 µF between Pin 6 and ground. - Pin 3 (Out A) goes through a 4.7 kΩ resistor to the base of Q1 (BC547 NPN transistor). - Pin 3 also connected via a 100 nF capacitor to Pin 13 (Trigger B of Timer B). 3. Timer B (rest 10 seconds): - Pin 9 (Discharge B) and Pin 8 (Threshold B) connected together. - R2 = 1 MΩ between Pin 9 and +12V. - C2 = 10 µF between Pin 8 and ground. - Pin 12 (Out B) can be optionally used to block retrigger of Timer A. 4. Relay driver stage: - Q1 = BC547 NPN transistor. - Base connected through 4.7 kΩ resistor to Pin 3 (Out A). - Emitter to ground. - Collector connected to one side of the relay coil. - Other side of relay coil connected to +12V. - A diode 1N4007 placed in parallel with the relay coil (cathode to +12V, anode to collector of Q1). - Relay contacts switch the +12V supply to the electric fence energizer. 5. Contact detector: - Shunt resistor ≈0.1 Ω placed in series with the fence output. - Q2 = BC547 NPN transistor, base connected to the shunt, emitter to ground, collector to Pin 2 (Trigger A). - When current flows through the shunt, Q2 provides a trigger pulse to Timer A. Please draw the schematic in a standard style with components connected by straight lines, not in block diagrams. Show clear pin numbers of the NE556 and all external components.... show moreSecret Crimson Hoverboard
Circuit Overview The circuit you're describing is a digital counter that uses an LDR (Light-Dependent Resistor) and a transistor to detect wheel rotations. The counter's output is then displayed on a seven-segment LED display. Here's a breakdown of the components and their roles: 1. Wheel Rotation Detection (LDR and Transistor) * LDR: The LDR acts as a sensor to detect changes in light intensity. You can mount it on the wheel' or near it, with a reflective or non-reflective surface attached to the wheel. As the wheel rotates, the LDR will be exposed to alternating light and dark conditions, causing its resistance to change. * Transistor: The transistor (e.g., a 2N2222 NPN BJT) is used as a switch or amplifier. The changing resistance of the LDR is used to control the base current of the transistor. When the LDR's resistance drops (more light), the transistor turns on, and when the resistance increases (less light), the transistor turns off. This converts the analog change in light into a digital ON/OFF signal (a pulse). 2. Counter (7490) * 7490 IC: This is a decade counter, meaning it can count from 0 to 9. The output of the transistor (the pulses) is fed into the clock input of the 7490. Each pulse represents one rotation of the wheel, and the 7490 increments its count accordingly. The 7490 has four outputs (Q0, Q1, Q2, Q3) that represent the BCD (Binary-Coded Decimal) equivalent of the count. 3. BCD to Seven-Segment Decoder (7446) * 7446 IC: The 7446 is a BCD-to-seven-segment decoder/driver. Its job is to take the 4-bit BCD output from the 7490 and convert it into a signal that can drive a seven-segment LED display. It has seven outputs (a, b, c, d, e, f, g), each corresponding to a segment of the LED display. 4. Seven-Segment LED Display * Seven-Segment Display: This display is used to show the count. The 7446's outputs are connected to the corresponding segments of the display. 5. Power Supply and Other Components * Power Supply: A regulated DC power supply (e.g., 5V) is needed to power all the ICs and components. * Resistors: Resistors are used for current limiting (e.g., for the LDR and the LED display) and biasing the transistor. * Capacitors: A capacitor might be used for debouncing the signal from the transistor to prevent multiple counts for a single rotation. Conceptual Connections Here is a step-by-step breakdown of how the components would be connected: * LDR and Transistor: * The LDR and a current-limiting resistor are connected in series across the power supply. * The junction between the LDR and the resistor is connected to the base of the NPN transistor. * The emitter of the transistor is connected to ground. * The collector of the transistor, with a pull-up resistor, becomes the output for the pulse signal. * Transistor to 7490: * The output from the transistor's collector is connected to the clock input of the 7490 IC. * The 7490's reset pins (MR and MS) should be connected to ground for normal counting operation. * 7490 to 7446: * The BCD outputs of the 7490 (Q0, Q1, Q2, Q3) are connected to the BCD inputs of the 7446 (A, B, C, D). * 7446 to Seven-Segment Display: * The outputs of the 7446 (a, b, c, d, e, f, g) are connected to the corresponding segments of the seven-segment display. * Crucially, you need to use current-limiting resistors (e.g., 330Ω) in series with each segment to protect the LEDs from high current. * The common terminal of the seven-segment display is connected to the power supply (for a common anode display) or ground (for a common cathode display). This setup creates a chain reaction: wheel rotation changes light, which changes LDR resistance, which turns the transistor on/off, generating a pulse. This pulse increments the 7490, and the 7490's output is decoded by the 7446, which then displays the count on the seven-segment LED.... show more2SD882PU
30V 1W 30@20mA,2V 3A SOT-89 Bipolar Transistors - BJT ROHS #CommonPartsLibrary #TransistorBJT #NPNSchmitt Trigger
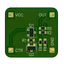
This is a simple project of a Schmitt trigger built on 2 NPN transistors. For use in boards, there are 4 foams that allow you to use it on a breadboard #NPN #triger #project... show more